Learn about Simple interest and Compound interest:
We have come across the term interest in many places and situations.
Any small amount of money borrowed is accompanied by a certain percentage of interest in banks or other private organizations.
When analyzed, every bank has a different way of collecting interest from their customers. Primarily it will be collect as
a. Simple interest
b. Compound interest
There would be a lot of questions running through your head as to why this is, what's the difference between the two types, and so forth. In this article, we will find all the answers.
Interest: Definition
What exactly is meant by interest.
The benefits of borrowing money from any organization also come with a small payback. This is what interest means.
An interest charge is a percentage of the borrowed principal amount that is imposed by the bank or organization. But the same can benefit you when the bank uses your money and pays you interest.
The exact definition varies and is dependent on whether the money is being borrowed or deposited.
What is Simple Interest?
You borrow a loan from the bank and the bank collects a percentage of charge on the principal amount borrowed. Simple interest refers to this percentage.
When a loan is borrowed, it is not the same amount that is returned. The rate that is charged is in terms of simple interest. Simple interest is always calculated on the principal amount that is being borrowed.
The reason for preferring simple interest is because, it is easy and convenient to collect charges from the borrower. Throughout the overall loan period the principal amount remains the same and so the simple interest that is paid also remains constant.
How to calculate Simple Interest?
Calculating simple interest is not a difficult task. Just a simple formula to calculate the charges for the loan that you have borrowed.
The method of computing is by multiplying the interest rate that is decided by the bank to the total principal amount and overall period of time (i.e., years). On calculation SI = PNR / 100
P - Principal amount of loan that is borrowed from the bank
N - Number of years for the payment.
R - Interest rate that is charged on the principal amount
To give an example,
P = Rs.15000 N = 5 years R = 8% SI = 15000138 / 100
So the payment that has to be made every month for 5 years is Rs. 6000. This interest payment remains constant throughout as the principal amount also remains the same.
Benefits of Simple interest:
- The reason for choosing simple interest is that, it benefits the one who borrows money.
- The interest and the principal amount don't change, making it easier to pay back the money that is borrowed.
- It is easier and simpler way to calculate the interest that is involved with the loan that is given by the bank.
- It is not necessary to worry about the rise in interest rates after a period of time.
- The compounding of interest is not necessary with simple interest and when investments are made the cash flow is constant and straightforward.
What is compound interest?
All that we have seen is how interest is charged on the principal amount. But in certain situations, interest will also be charged on the previous interest amount and this is referred to as compound interest.
Though simple interest is easy to calculate and the amount payable is less, compound interest is found to be advantageous for investments and deposits. If the interest earned from the deposit generates interest, then the depositor has a better chance of gaining more than simple interest.
People usually choose compound interest to get an exponential return on the investment they made. The frequency of interest can be set by the bank, such as daily, weekly, monthly, or annually.
How to calculate compound interest?
Compound interest is calculated by multiplying the principal amount with one plus the interest rate raised to the power of the duration and finally subtracted from one.
CI = P [(1+i)n-1]
CI - Compound Interest
P - Principal amount that is deposited or borrowed.
i - Interest that is charged on the principal amount
n - Compounding period, i.e., daily, monthly, quarterly, half-yearly or annually.
To give an example,
P = Rs. 7000 i = 6% n = 10 years Using the formula, CI = 7000*[(1+0.06)10-1]
The compound interest in this case would be Rs.5,536. So the total amount of the investment at the end of the duration will be Rs. 12,536.
Benefits of compound interest:
- As interest gains interest in compound interest, the total amount gained at the end of the period is always higher than the principal amount.
- When the duration of compounding years is higher then the investment amount also increases at the end.
- When investments are made in compound interest, they multiply faster and have higher values.
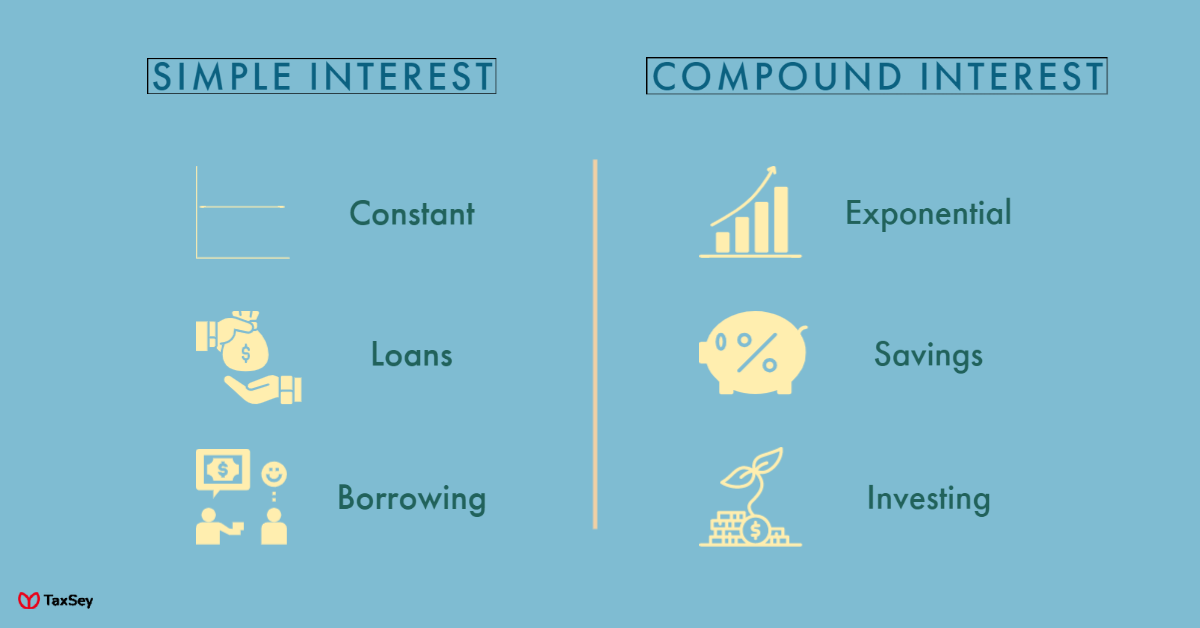
Compound interest vs Simple interest:

Both simple and compound interest are used at various sectors and categories in banks and other financial institutions. It is how far both the borrower and lender is benefited at different situations.
For instance, when you are borrowing a loan it is best to have simple interest as the interest rate remains constant. At the same time if you are investing the money then you could go for compound interest for multiplying what you deposit.
If you want your savings or investments to grow in a short period of time, then the best way by using compound interest. But when the same is charged on loans, it will be hard for the borrower to pay it back.
With simple interest that is not the case, even if it doesn’t give back great returns the rates remain constant.
Areas where simple interest can be used,
- Automobile loans
- Educational loans
- Mortgages
- Other short term loans.
Areas where compound interest can be used,
- Mutual funds
- Fixed deposits
- Savings account
- Credit cards
Conclusion:
Simple interest and compound interest mean totally different things in different situations. It is how you use it and how you gain value from it that matters.
Choosing SI on investing and CI on loans are both big mistakes that anyone can make. So there has to be a detailed and clear explanation of how it works and where it should be used.
Compounding world works differently. When money is borrowed, an extra is paid but the same money when invested makes you a bit more rich. It is how you use it and borrow it.
Hence, now that you have a clear mind, you can make decisions and choose the interest that benefits you most.
Frequently Asked Questions
The goods and services tax (GST) is a value-added tax (VAT) levied on most goods and services sold for domestic consumption.