Debentures: Introduction
Borrowing money, raising funds, and investing is how the business world works. There could be different ways to borrow money, like getting loans, using collateral, approaching finance companies and much more.
What is a Debenture?
Lending money can be done through various resources and ways. Banks, venture capitalists, and financing companies have their own rules and procedures for lending money to small businesses.
Speaking about debenture, it is a form of document or legal certificate that is produced when you borrow money from another firm. It should be noted that, as a holder of debentures, there is no need for securities such as collateral.
Then how do debentures work without any security?
Debenture actually acts as the security document for the money that is being issued by the company. Repayment of the loan is truly dependent on the creditworthiness of the issuing party.
Typically, companies or individuals borrow money in the form of debentures to raise capital and funds, because the loan doesn't need to be secured.
Difference Between Shares and Debentures
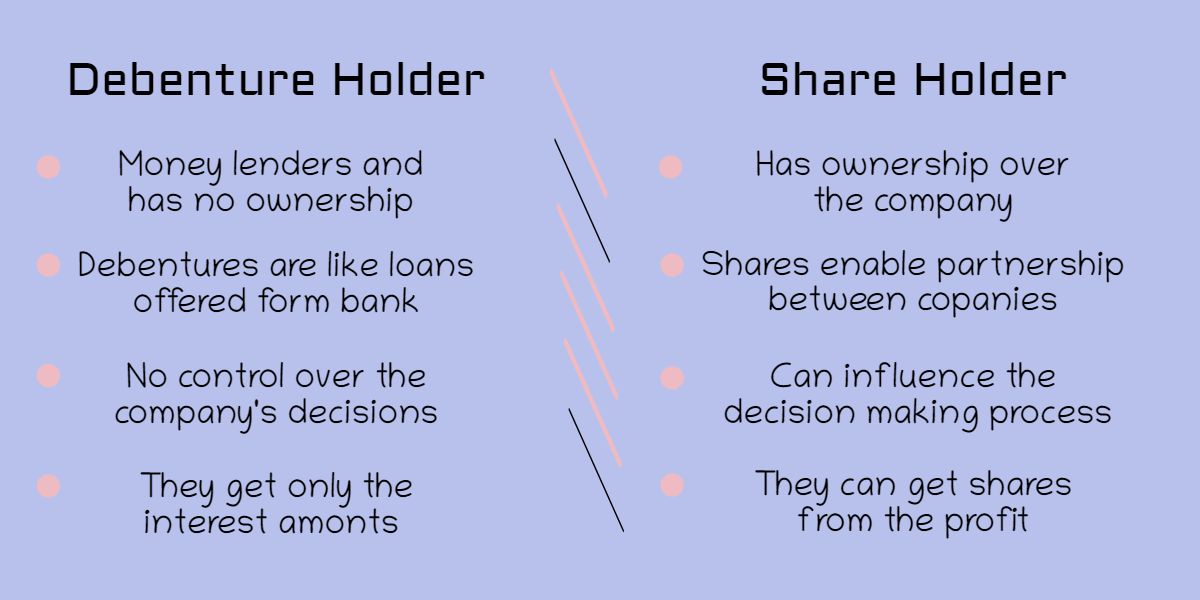
Let’s briefly look at the terms of shares and debentures.
Individuals or companies can buy shares when they want to form a partnership. In simple words, one can claim ownership over a small portion of the company and are called shareholders.
In the past, we discussed that debentures are debt documents issued when companies give loans to other organizations. Here the issuers are treated as debenture holders.
Shareholders and debenture holders are usually confused with each other.
In larger terms the difference is that, a shareholder can have complete authority over the functions of the company, while the debenture holders are just money lenders. Since the security levels with debentures are relatively low, this makes the process easier.
Elements of Debenture:
Debenture certificates contain certain details that act as proof of the money that is transferred between the two parties.
1. Loan Amount:
Debentures are issued as an agreement to the loan amount that is being issued. Therefore, the details of the money that must be paid by the borrower are listed.
2. Declaration:
This is sort of a guarantee between the parties involved about the money that is being borrowed.
3. Face value:
The amount that has to be repaid doesn’t remain the same as the initial rates. So face value is the amount of money that has to be paid at the end of the maturity date of a debenture.
A debenture's face value is calculated based on the annual interest amount, interest rate, maturity time, and principal value.
4. Interest rates:
Similarly to loans, debentures also have fixed interest rates. However, the rates and payment terms vary from issuer to issuer. This rate is referred to as a coupon rate because it is associated with debentures.
5. Repayment schedule:
Repayment schedule specifies when interest rates, principal amount, and other payments should be made to the issuer.
6. Maturity data:
Maturity data is the end of the agreement period. But at the end of the maturity period, the borrower has to settle all the loan amount including the interest rates.
7. Credit ratings:
Credit rating evaluates and defines the ability of the borrower to return the money back to the organization. It is this factor that estimates the principal amount involved in a debenture agreement.
8. Priority of repayment:
The reason for debentures is to raise capitals and funds. The company borrowing money might have other commitments and liabilities that need to be settled.
So the priority of repayment defines when the debenture loan will be settled among other loans and liabilities.
Who can issue a debenture?
Debenture is a bond that is issued between two firms. Generally, the agreement is made between two businesses, companies, or individuals seeking funds and capital.
The issuing company is referred to as the debenture holder and the cash flow between the parties depends entirely on the value, creditworthiness and reputation of the issuer.
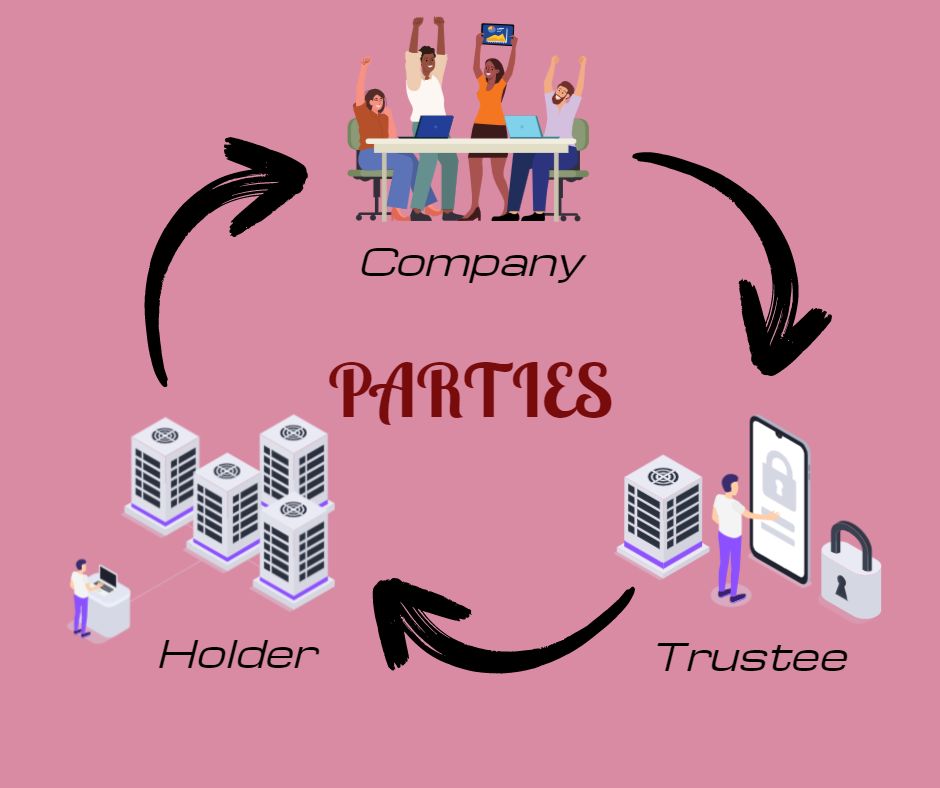
Parties involved in this process are categorized accordingly.
A. Company:
Companies are the ones who borrow money to raise funds. The reason to request a debenture bond can be due to various reasons. When the assets are laid as security for other liabilities, then the company can ask for a debenture, as it is not a bond by security.
B. Trustee:
Trustees serve as the intermediary between the parties to an agreement. They are responsible for signing contracts. Companies usually sign contracts in the name of a Trustee.
C. Debenture holders:
Debenture holders issue money to the companies. It can be government organizations, business firms or individuals with a high credit value. On lending money, they issue a debenture certificate which acts as proof for the contract.
Types of Debentures:
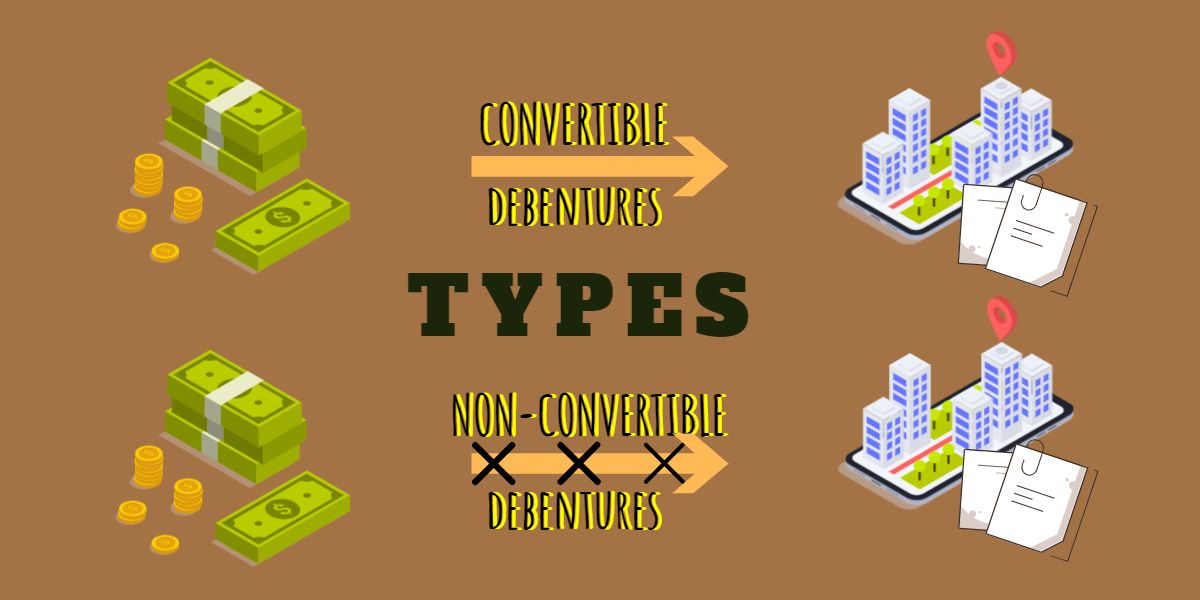
Debentures issued could be of various types depending upon the parties involved, credit value, needs and requirements. Accordingly they are classified into,
1. Convertible debenture
A debenture holder usually does not own any shares of the company, since they are merely money lenders. But when the agreement is signed in terms of convertible debentures, then the holders can transform their money into shares anytime.
The holders of convertible debentures have the option to convert the money into shares when the company shows success and generates great profits.
In this case, they can be both debenture holders and share holders, i.e., they hold a percentage of the company. Additionally, they receive interest on the principal amount.
Further classification includes,
a. Partially Convertible: The loan that is lent by the holder is not completely converted to shares at the time of conversion period. Only part of the debt is converted into shares, while the rest remains as a debenture until maturity.
b. Fully Convertible: At the time of conversion period, the entire debenture amount is converted to share and the debenture holders become share holders.
c. Optionally Convertible: The amount may or may not be converted to shares during the conversion period. By viewing the progress, holders can decide whether to convert their shares or not
2. Non-Convertible Debentures
Here the loan amount remains as such and cannot be converted into shares. But the holders can set their interest rates for the principal amount. Interest rates for non-convertible debentures are usually higher than those for convertible debentures.
Advantages of Debentures:
- Fixed interest rates: The issuing companies offer a nominal and fixed interest rate for the total principal amount until the maturity period.
- Unsecured loans: The companies are benefited as it is collateral free. Even when the company’s assets are backed up at other loan payment, debenture can be issued by other individuals.
- Lenders get benefited: Debentures are a great advantage for the lenders, as they can even set a higher interest rate compared to other loan and bond agreements.
- Minimum risk: As the holders doesn’t hold any ownership over the company, even at the times of loss there isn’t any risk for the lenders. At the same time, they get paid by the terms of the agreement.
- Conversion: The conversion process from loan to shares is easier and the decision can be made during any time.
Disadvantages of Debentures:
- No profit: Debenture holders doesn’t get any profit like shareholders. Its just the loan amount that is repaid along with interest.
- Risk to investors: Interest rates are fixed throughout the debt period, which makes it risk for the investors. When the inflation rates are high in the future, the fixed interest rates will be very low and the holders may face a loss.
- Financial burden: When the company has no profits, then it will be difficult to repay the loan and interest.
Conclusion:
At times, when thinking about the safety of assets and company shares it is always better to borrow money which is not secured by collateral. Debentures are a great solution to this problem.
Not just this, it is also a great investing option. Its long term, no need to worry about the losses of the company. But still, when the value raises and interest rates are low it will cause a loss.
Debentures has its own pros and cons. Depending on the company’s requirements and issuer’s creditworthiness, debenture is a great option that can be preferred over other forms of borrowing money.
Frequently Asked Questions
The goods and services tax (GST) is a value-added tax (VAT) levied on most goods and services sold for domestic consumption. The GST is paid by consumers, but it is remitted to the government by the businesses selling the goods and services.